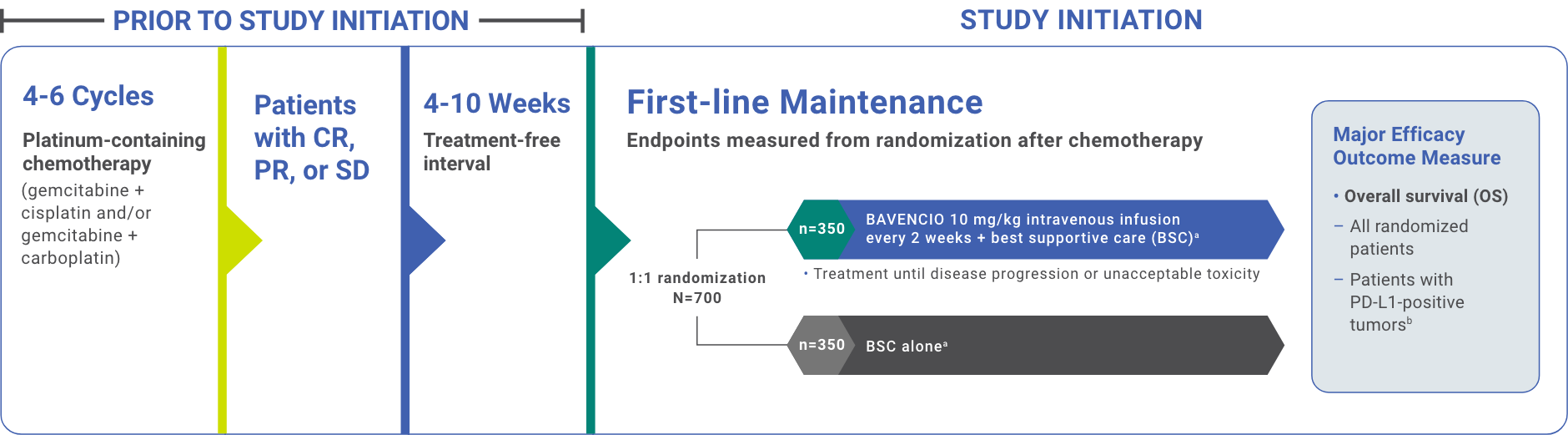
Phase 3, randomized, open-label, multicenter study in patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (UC) that did not progress with first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy (N=700)1,2
Study Design1,2
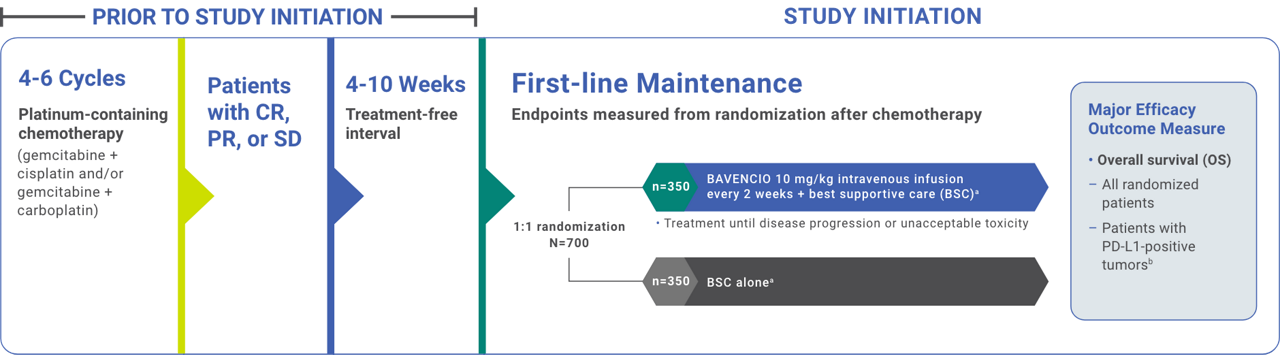
aBSC was administered as deemed appropriate by the treating physician, and could include treatment with antibiotics, nutritional support, and other patient management approaches with palliative intent (excludes systemic antitumor therapy).1
bPD-L1 expression was assessed in tumor samples using the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) assay.1
CR=complete response; PD-L1=programmed death ligand-1; PR=partial response; SD=stable disease.
Eligibility Criteria
- Unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic UC
- ≥1 measurable lesion defined by RECIST v1.1
- 4-6 cycles of platinum-containing chemotherapy (gemcitabine + cisplatin and/or gemcitabine + carboplatin)
- ECOG PS 0 or 1
Exclusion Criteria
Patients with autoimmune diseases or medical conditions requiring systemic immunosuppression
ECOG PS=Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Status; RECIST=Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors.
Stratified by best response to chemotherapy (CR/PR vs SD per RECIST v1.1) and site of metastasis (visceral vs non-visceral) assessed at the time of initiating first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy2
- Administration of BAVENCIO was permitted beyond RECIST-defined disease progression if the patient was clinically stable and considered to be deriving clinical benefit by the investigator
- Assessment of tumor status was performed at baseline, 8 weeks after randomization, then every 8 weeks up to 12 months after randomization, and every 12 weeks thereafter until documented confirmed disease progression based on BICR assessment per RECIST v1.1
BICR=blinded independent central review; CR=complete response; PR=partial response; RECIST=Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors; SD=stable disease.
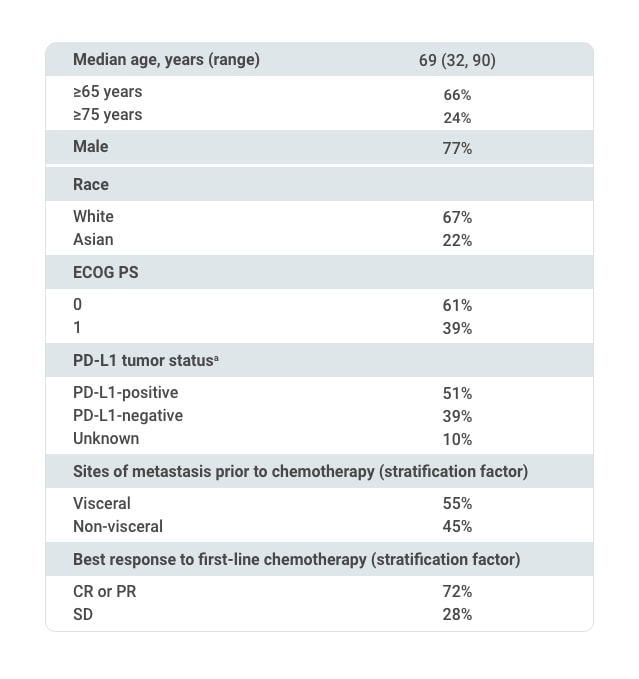
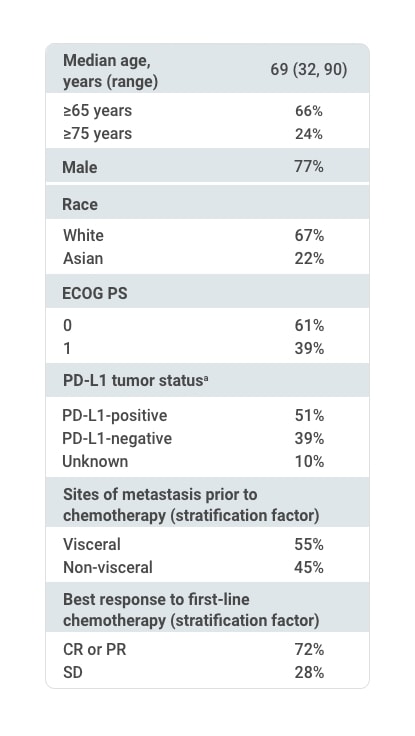
Selected Baseline Characteristics of All Randomized Patients (N=700)1,2
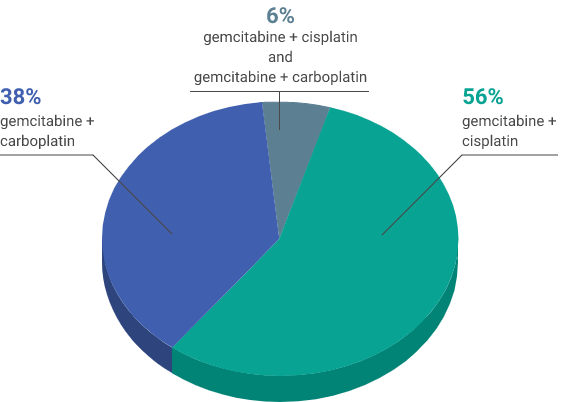
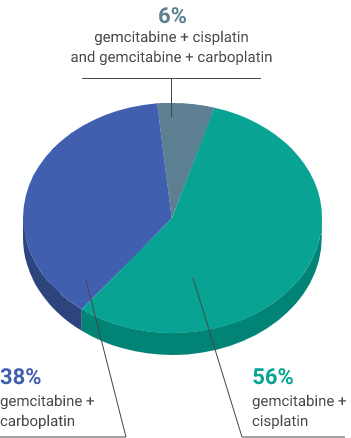
First-line chemotherapy regimen
aUsing the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) assay, PD-L1-positive status was defined as PD-L1 expression in ≥25% of tumor cells or in ≥25% or 100% of tumor-associated immune cells if the percentage of immune cells was >1% or ≤1%, respectively. If none of these criteria were met, PD-L1 status was considered negative.1
CR=complete response; ECOG=Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; PD-L1=programmed death ligand-1; PR=partial response; PS=performance status; SD=stable disease.
References: 1. Powles T, Park SH, Voog E, et al. Avelumab maintenance therapy for advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(13):1218-1230. 2. Bavencio Prescribing Information. EMD Serono, Inc.; 2024.